Field - Wireless Monitoring Solution for Geological Disasters
User Requirement Analysis:
The user is a geological disaster prevention monitoring department. They need to install a series of monitoring equipment in a certain area prone to geological disasters in the wild, and also need to transmit the data from these monitoring devices to the monitoring command center. The distance between the monitoring command center and the site is approximately 40-50 kilometers. Using the wired transmission method to send the monitoring data back would require a large amount of manpower, material resources and financial resources. The setup process is long and the maintenance cost is high. This solution is no longer practical. Therefore, the user needs to use a wireless method to transmit the data back. The situation at the site is as follows:
The target location is approximately 50 kilometers away from the monitoring center. Moreover, the location being monitored cannot be directly viewed from the monitoring center (it's not in line of sight). The location being monitored has no 4G coverage and no power supply.
It is necessary to monitor the water flow data at the target location to issue early warnings in case of floods; it is also necessary to monitor the data of landslides; conduct real-time video monitoring (as the data volume of video monitoring is large, the transmission bandwidth occupied is high, and the power consumption of video monitoring cameras is also high. The implementation will be decided based on the on-site situation and the amount of solar power supply in the future).
Wireless Solution Thinking and Design:
Based on the above description of the on-site situation by the user, the use of wireless transmission has been confirmed. However, since there is no 4G operator signal at the site, 4G equipment cannot be used for transmission. Therefore, a digital wireless bridge method must be adopted for long-distance transmission. Additionally, the monitoring points at the front end and the relay transmission points do not have power supply. Thus, in the scheme design, solar power supply solution needs to be adopted for power supply. If necessary, wind turbines can also be used for power supplementation.
Regarding the selection of digital wireless transmission equipment, our company recommends the use of the following two models for this application scenario: the TQ-5040G series and the TQ-5823WJ series. According to the user's application site, the wireless transmission topology diagram of this solution is shown in the following figure:
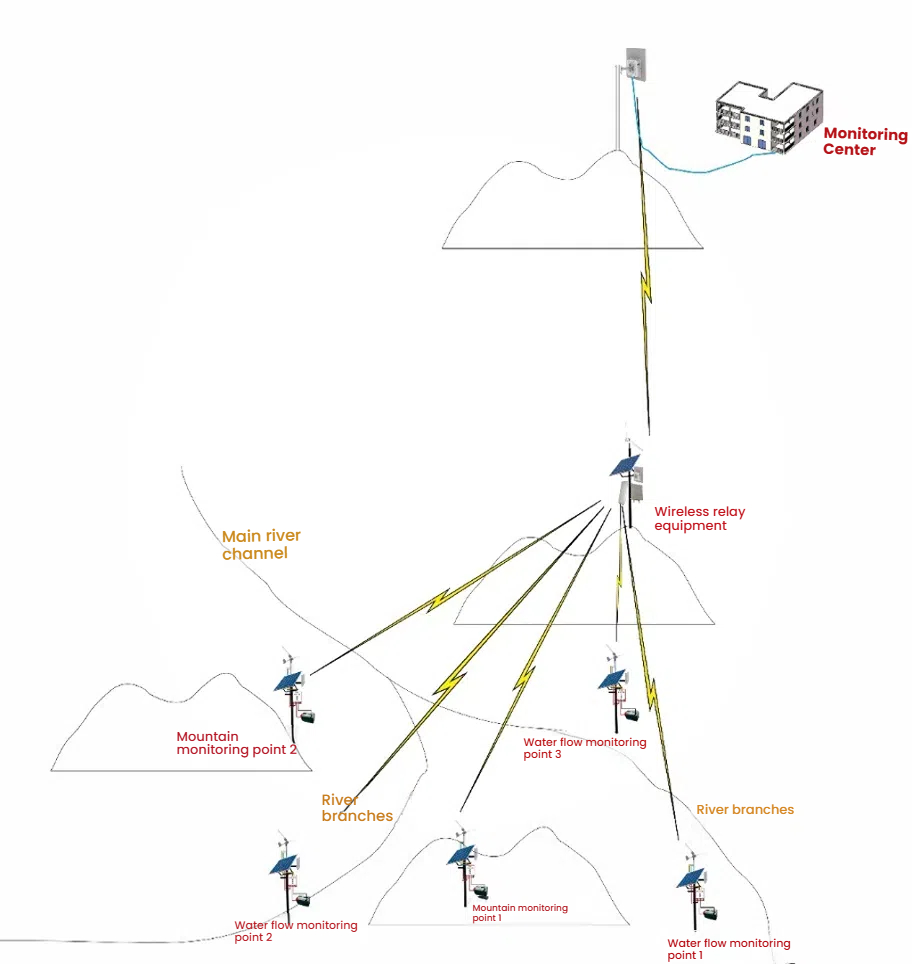
According to the scheme diagram mentioned above, the wireless devices installed at the monitoring points in the front river valley and the landslide monitoring points are generally installed at relatively low positions. Under normal circumstances, they cannot directly view the monitoring command center at a distant location. Therefore, around some nearby monitoring points, a relatively high position needs to be selected as a relay transmission point. First, the data from the front monitoring points is aggregated using the wireless devices at the relatively high relay transmission point, then a pair of long-distance digital bridges is used to transmit it to a relatively high mountain near the back-end monitoring center, and finally, it is transmitted to the monitoring command center via a wired connection.
Our company's two digital wireless transmission devices are suitable for meeting the transmission requirements in the above-mentioned scheme. The TQ-5040G is a medium and short-range wireless transmission device, which is suitable for transmitting and aggregating the monitoring data from the front end to the relay transmission point, and can be used as a branch summary device. After the monitoring data from the front end is aggregated, the data is transmitted to the monitoring command center 50 kilometers away by the long-distance device TQ-5823WJ, which is equipped with a high-gain directional antenna.
Equipment required for the node:
Water flow monitoring points 1, 2, 3: TQ-5040G, integrated wind-solar power generation and storage system, water flow data collection sensor;
Mountain monitoring points 1 and 2: TQ-5040G, integrated wind-solar power generation and storage system, mountain data collection sensor;
Wireless relay points: TQ-5040G-W, angle antenna, TQ-5823WJ, dish-shaped antenna, switch, integrated photovoltaic power generation and storage system;
Monitoring Center: TQ-5823WJ, dish antenna
Realization process:
The water flow monitoring points and the mountain body monitoring points use the SF-5040G to transmit the data collected by the sensors to the wireless relay equipment point located at a high position. At the wireless relay equipment point, there is the TQ-5040G-W which cooperates with an external angle antenna to receive the sensor information from the water flow and mountain body monitoring points. Then, the information is connected to the long-distance wireless bridge TQ-5823WJ through the switch and transmitted for emission, at a receiving point 50 kilometers away, a similar TQ-5823WJ (with the transmission path of the TQ-5823WJ device being unobstructed) is set up. Using a data cable or optical fiber, the received information is transmitted to the monitoring center.
In this plan, if a real-time video monitoring system is to be added later, it can be achieved by simply adding cameras at the monitoring points and increasing video storage equipment at the monitoring center on the basis of the existing wireless network, without the need for additional transmission equipment.
Introduction of Wireless Devices
3.1 TQ-5040G
Product appearance:

TQ-5040G high-power outdoor wireless bridge, suitable for wireless network connection services in harsh outdoor environments, provides high-bandwidth network connections and multimedia IP data transmission requirements for enterprises and industrial users. It is not only suitable for network transmission but also meets the needs of large-scale IP monitoring. The TQ5040G high-power outdoor wireless bridge equipment can effectively connect two distant nodes using the built-in 18dBi gain antenna. The transmission distance can reach 8km and the transmission bandwidth can reach 80-90Mbps, providing wireless transmission quality comparable to wired networks.
The TQ-5040G high-power outdoor wireless bridge device supports AP mode, WDS mode, ClientBridge + Repeater AP mode. The combination of different modes can achieve different functions, and it can perform point-to-point transmission and point-to-multipoint transmission. In WDS mode, a 1-to-8 (fill in 8 different MAC addresses) connection form can be realized. In AP mode, it can theoretically support 32 clients. This device supports both Chinese and English interfaces, is easy to operate, eliminates cumbersome operation methods, making debugging faster and more convenient, facilitating rapid deployment, and is very suitable for engineers to quickly master. The power supply adopts a wide voltage input design of DC 12~24V, and the actual power consumption of the device is less than 5W. In the absence of mains electricity in the field, it can flexibly be combined with various power supply methods such as batteries, solar energy, wind energy, etc. for operation.
3.2 TQ-5823WJ
Product appearance:

The TQ-5823WJ series of high-capacity long-distance license-free frequency band point-to-point digital wireless bridge is based on the proprietary point-to-point wireless protocol of dynamic TDD. Data is encapsulated into large packets for transmission, which improves transmission efficiency (forwarding capacity: 35,000 PPS), increases bandwidth utilization (spectral utilization: 7.5 bits/Hz), and enhances the transmission distance, throughput, and PPS forwarding capacity of the system. The transmission delay of the system is less than 2ms, enabling real-time transmission of voice, video and other data. It adopts the 2×2 MIMO breakthrough technology to achieve a throughput of up to 220 Mbps (110 Mbps full duplex), with excellent PPS data packet processing capabilities and high anti-interference ability.
The TQ-5823WJ series products can be applied to telecommunication-level point-to-point network applications. They are ideal devices for dedicated line access or backhaul applications (including VOIP and other small data packet transmission applications). This series of products achieve an extremely high spectral utilization rate of 7.5 bit/Hz by combining flexible channel bandwidth (20 or 40 MHz) and specially customized long-distance transmission private protocols. The products are equipped with dual-polarization antennas (TQ-5823WJ) or come with 2 N-type connectors (TQ-5823WJ), and the sturdy cast-aluminum casing reaches IP-67 protection level.
The TQ-5823WJ/TQ-5823WJ-W products integrate a series of advanced software mechanisms, which can provide the best point-to-point connection performance for high-throughput and long-distance link applications. The proprietary point-to-point communication mechanism utilizes dynamic time division duplex (TDD) technology to dynamically allocate bandwidth for the required transmission direction, thereby improving link efficiency and significantly reducing the impact of transmission distance on link throughput. Our point-to-point products also adopt selective retransmission ARQ technology to enhance error correction capabilities, optimize data traffic, and enable the equipment to achieve very high throughput even in large bandwidth, long-distance, and even interference conditions.
The built-in radio frequency module of the brand-new WJ series products has an emission power of 28 dBm (+/- 2 dBm), and even at the highest modulation mode (MCS 15), it can still reach 23 dBm (+/- 2 dBm). Thus, a stable long-distance link can be established using the built-in antenna. The product is equipped with a gigabit Ethernet port and supports the 802.3af standard, making it more flexible and convenient to use. At the same time, it is equipped with electrostatic protection in accordance with the IEC 61000-4-2 (ESD) standard and surge protection in accordance with the IEC 61000-4-5 (Surge) standard.
Due to the product's features such as high bandwidth and high stability, this equipment is widely applied in fields like forest fire prevention, island monitoring, and large data transmission in mining areas and factories.








