Design Scheme of Video Monitoring Optical Fiber Transmission System for Ordos Expressway
In recent years, with the development of society, security technology has been constantly maturing and improving. Security is moving towards networking, high definition and intelligence. The video surveillance system of expressways is no exception. However, the expressway monitoring system is large-scale, with long distances and complex signals, which puts forward higher requirements for the stability and flexibility of the application of the system. Therefore, to achieve networking, high definition and intelligence of the expressway video surveillance system, it is of paramount importance to build an intelligent, stable, practical, advanced, reliable, scalable and flexible optical fiber transmission system. The scheme proposed in this paper is an optical fiber transmission scheme designed for the expressway in Ordos, Inner Mongolia.

1. Customer Requirements
2.1 System Composition
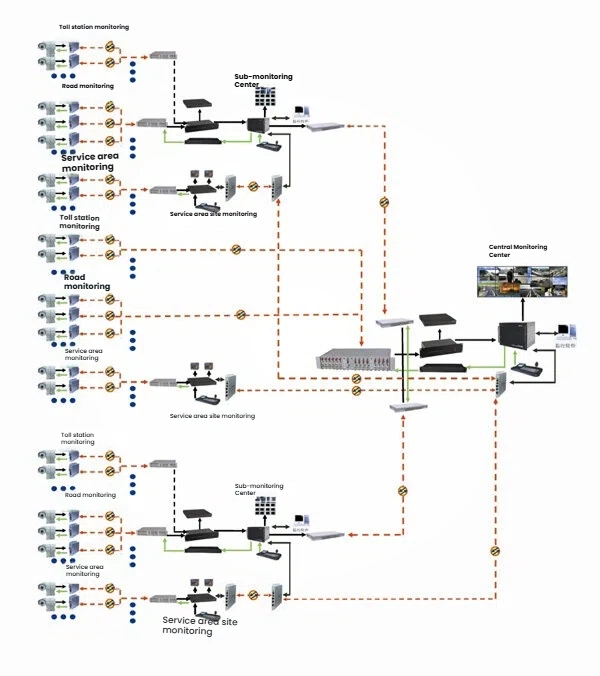
Based on the actual demand situation, the construction of the video monitoring series of optical fiber transmission system for expressways in Ordos City mainly includes: one main monitoring management center, three sub-monitoring management centers (one of which is set as the main monitoring center), seven highway service areas (located 2-3 kilometers away from both sides of the expressway), and seven toll stations, all of which are arranged near the seven pairs of highway service areas. All data from the seven pairs of highway service areas and the seven toll stations need to be uploaded to the corresponding sub-monitoring centers. All data of the sub-monitoring centers can be retrieved, monitored in real time and controlled by the main monitoring center.
1. General Monitoring Management Center:
The center of the video monitoring series fiber optic transmission system for expressways in Ordos City. It manages and monitors a total of 510 video images from 3 subordinate sub-monitoring centers, as well as nearly 20×7 video images from toll stations, and has the ability to conduct real-time detection and control of interval speed measurement data.
2. Sub-monitoring Management Center:
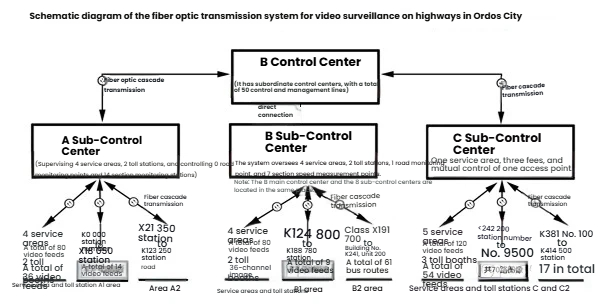
The monitoring management center at point K19+650 (referred to as A sub-control center) has 74 road video monitoring points. Among them, there are 14 front-end points, 59 rear-end points, and 1 side-point. It also includes 2 service areas, each with 20 video cameras, totaling 80 cameras. Among them, the stake mark (location) of the 2 service areas are K19+650 and K101+830. Therefore, the total number of video channels of the A sub-control center is 154.
The monitoring management center at the point K135+100 (the main monitoring management center is set up here at this sub-control center, so this place is called B main control center) contains 71 road video monitoring points. Among them, there are 9 front-end points and 61 rear-end points at the A sub-control center, and 1 side-point. It also includes 2 service areas, each with 20 video cameras, totaling 80. Among them, the two service areas are located at the following stake mark: K135+100 and K189+950. Therefore, the total number of video channels at B main control center is 151.
Point K380+100 is the monitoring management center (C monitoring center). The C monitoring center contains 88 road video monitoring points, among which there are 70 front-end points in the A monitoring center, 17 rear-end points, and 1 side-point. It also includes 3 service areas, each with 20 video cameras, totaling 120. Among them, the mileage numbers of the 3 service areas are: K247+200, K313+700, and K380+100. Therefore, the total number of video channels of the C monitoring center is 208.
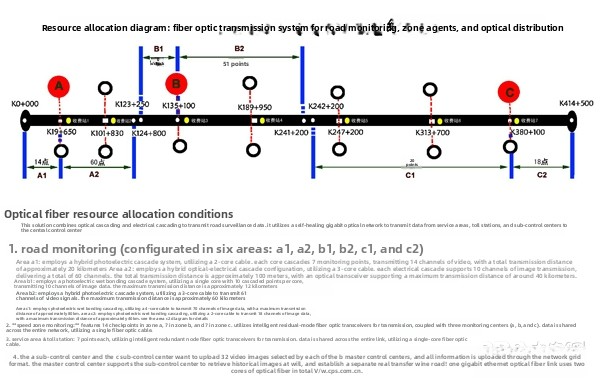
The A and C control centers are connected to the management center through a 2-core optical fiber, forming a star-shaped transmission network. The monitoring video images in the system are uploaded or retrieved using one core via an intelligent gigabit optical network. Additionally, one core is used to transmit any 32 non-compressed video images from the A and C control centers to the main control center in real time. Given the long distance between the control centers and the main control center, the transmission distance is extended by adding nodes. This expressway includes 7 pairs of service areas and 7 toll stations, all of which use an intelligent gigabit optical network for uploading or retrieving data. They use one-core optical fiber. Apart from video surveillance, each section also contains traffic guidance and interval speed measurement. The traffic guidance uses RS485 to transmit data and is located beside the video surveillance points. Therefore, by setting up optical transceivers at the video surveillance points and adding RS485 transmission channels, it is sufficient. Interval speed measurement uses Ethernet data transmission. Due to the limited optical fiber resources, only a single-core multimode optical fiber is provided. With a large number of transmission nodes, a gigabit intelligent ring network Ethernet optical transceiver is used for transmission.
The video monitoring series optical transmission system for expressways in Ordos City adopts a distributed and multi-level management mode. The sub-control centers and the main control center are connected through a star-shaped transmission network formed by 2-core optical fibers, and the sub-control centers and the service areas, toll stations are also connected through 1-core optical fibers to form an intelligent redundant gigabit shared optical network. The transmission distance of the expressway is long, and the monitoring points are highly dispersed. Therefore, this transmission scheme adopts the optical-electrical cascading method and applies the CWDM wavelength division multiplexing technology to solve the problem of insufficient optical fiber resources and the scattered distribution of monitoring points. This scheme has three levels of signal transmission management. The first level is the main control center, which implements real-time monitoring of road monitoring images, and all recorded image data can be uploaded to the main control center or any historical images can be retrieved; the second level is the sub-control center, which manages various signals within its jurisdiction and provides all signals of that area to the superior main control center; the third level is the service areas, toll stations, and road monitoring points. The service areas centrally manage the monitoring video signals and pan-tilt control signals of this area, and the toll stations centrally manage the monitoring video signals of their own areas. They also upload images and other signals to the sub-control center and the main control center through the shared full-speed gigabit intelligent optical network jointly established with the service areas. The monitoring points centrally upload the video signals, pan-tilt signals, and nearby interval speed measurement or traffic guidance data signals of this point to the subordinate sub-control center. The three levels of communication adopt optical-electrical cascading and apply the CWDM wavelength division multiplexing technology to ensure that the signals transmitted from the lower level to the upper level are in a stable and efficient state.
2.2 Product Application Recommendations
This plan focuses on the specific requirements of the video monitoring series of optical fiber transmission systems for expressways in Ordos City. Based on the design requirements such as intelligence, stability, practicality, advancement, reliability, scalability, flexibility and economy of the system, it is recommended to use the ONV non-compressed video digital electro-connection optical transceiver equipment, ONV non-compressed video digital optical transceiver equipment, and ONV intelligent redundant node optical transceiver equipment from Shenzhen Guangwangshi Vision Technology Co., Ltd. for video transmission equipment.
The superiority of the product application design is manifested in the following aspects:
A) Standardization principle: The selection, debugging, installation and other stages of the equipment will strictly follow the quality management regulations. They fully comply with the requirements of the tender documents and the relevant standards of the country and industry, ensuring the stable, reliable and safe operation of the system.
B) Principle of Advancedness: In the system design, we fully take into account the development of image monitoring and video transmission technologies, and refer to the current development level of the video monitoring and image transmission industry to ensure that the system holds a leading position in China.
C) Safety and Reliability Principle: The system adopts a star-shaped network structure, uses optical cascading, employs CWDM wavelength division multiplexing technology, and utilizes different wavelengths to ensure that faults at each monitoring point do not affect the operation of other monitoring points, sub-control centers, and main control centers. It also uses electrical cascading, adopts the most advanced optical switch technology and electrical cascading technology. The electrical cascading technology superimposes and modulates the video signals and controls faults through the optical switch, ensuring that faults at the monitoring points do not affect the operation of other monitoring points, sub-control centers, and main control centers.
D) Scalability Principle: When designing this solution, the future scalability of the system was taken into account. The image business requirements were fully considered, and it was ensured that the system could meet the upgrade and expansion needs for a relatively long period of time without incurring a large amount of investment. Interfaces were also reserved for connecting the systems in the near and distant future.
E) Economic Principle: The entire transmission system should achieve a comprehensive balance in terms of advancement, openness, efficiency, practicality, reliability and stability. In addition to ensuring high real-time image transmission and dynamic stability of image services, the transmission system must also have a good performance-price ratio of the system.
F) Practicality: The scheme design meets the requirements of the monitoring system and fully takes into account the specific usage requirements of the system's image monitoring project.
G) Usability principle: Simple control; Easy fault diagnosis and isolation; Convenient for maintenance.
II. Solution
3.1 Overview of the Plan
This transmission system is networked in a star connection cascading manner. The central control center can achieve real-time monitoring of all images of the road surveillance, retrieve images or other information from any monitoring point, and realize unified control functions. Each monitoring point operates independently and is not affected by the working conditions of other monitoring points. Installation is simple and maintenance is convenient. This system adopts advanced wavelength division multiplexing technology, optical switch technology, electrical cascading technology, and intelligent self-healing technology. Only eight-core optical fibers are needed to enable the central control center to effectively switch and control images within the monitoring system and collect data required for road operation and provide effective traffic guidance.

3.2 System Composition
3.2.1 Overall Structure
The video monitoring series optical transmission system for expressways in Ordos City adopts a three-level networking method. According to the actual situation of the expressways in Ordos City, the central control center is the first level, the sub-control center is the second level, and the service areas and road monitoring points are the third level. The service areas or road monitoring points first collect nearby signals and separately connect them to the optical transceiver transmission equipment configured for that service area or road monitoring point. In the service areas and toll stations, local monitoring can be achieved simultaneously and the monitoring images can be uploaded to the sub-control center. The sub-control center centrally and uniformly manages the video and other signals collected from the service areas and road monitoring points. In addition to local monitoring, it also connects the gathered signals to the optical transceiver equipment configured for this sub-control center. The central control center uniformly monitors the signals uploaded by each sub-control center. The construction of the video monitoring series optical transmission system for expressways in Ordos City includes: three monitoring centers (one of which has both "sub-control center" and "central control center" functions), 7 pairs of service areas (three monitoring centers are distributed among 14 service areas, and the service areas are paired and distributed on both sides of the roads), and 7 toll stations (located near the service areas).
The video monitoring series optical transmission system for expressways in Ordos City covers the access, transmission, control of video signals and the unified management of other signals. It is the core subsystem of the expressway monitoring system. This project has the characteristics of decentralized front-end points, multi-level transmission, distributed management, complex lines, and high confidentiality requirements. Therefore, the way of video transmission directly determines the quality and effect of the entire monitoring system.
In this system, the video transmission between service areas/toll stations, road monitoring points, sub-control centers, and main control centers all utilize optical fibers as the transmission channels. The all-optical digital monitoring network designed in the scheme integrates digital non-compressed video encoding technology, optical private network communication technology, digital matrix technology, CWMD technology, optical crosstalk technology, electrical crosstalk technology, optical switch technology, and intelligent self-healing network technology. It addresses the characteristics of video transmission in highway monitoring systems and realizes full digital transmission and cross-switching, as well as front-end scalability. It represents a qualitative leap compared to traditional video monitoring networking methods.
3.2.2 Networking Mode
The central control center is at the first level, the sub-control centers are at the second level, and the service areas/toll station/road monitoring points are at the third level. A star-shaped distributed transmission network is formed using the existing optical fibers as the transmission channels.
By adopting an all-optical digital monitoring network, with multi-level transmission and unified management, a complete monitoring network has been established, which not only meets but also enhances the transmission capacity and network quality of the dedicated network.
The service area and toll station will centrally collect the video signals and control signals, not only for local monitoring but also for uploading to the superior centralized control center. The road monitoring points will only centrally collect the video signals, control signals and other nearby data signals of this point and upload them to the superior centralized control center via the ONV intelligent redundant gigabit optical fiber transceiver.
2. The sub-control center will consolidate the video signal and other signals, and in addition to achieving local monitoring, it will also uniformly upload the video signal and other signals to the main control center.
3. The central control center is connected to the sub-control centers through independent optical fibers (with two cores) to form a transmission network, enabling bidirectional transmission between the central control center and the sub-control centers.
4. The central control center is responsible for the switching, calling, control and transmission of image signals. It can directly call any signal from the central control center and implement the corresponding control.
The system topology diagram is shown in Figure 1:
The schematic diagram of the optical fiber transmission system is shown in Figure 2:
The schematic diagram of area division and fiber resource allocation is shown in Figure 3:
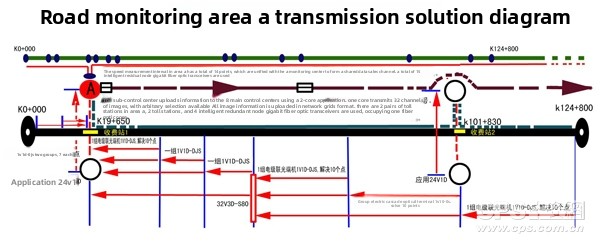
The schematic diagram of the transmission plan for Area A of the optical fiber transmission system is shown in Figure 4:
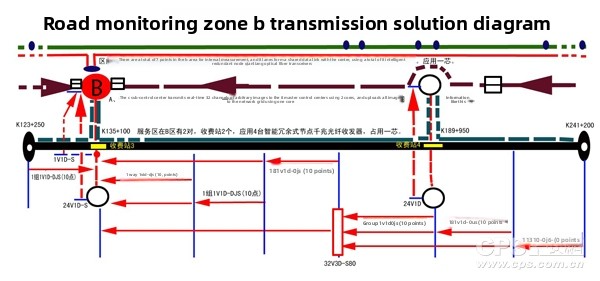
The schematic diagram of the transmission plan for Road B area of the optical fiber transmission system is shown in Figure 5:
The schematic diagram of the transmission plan for Road C area of the optical fiber transmission system is shown in Figure 6:
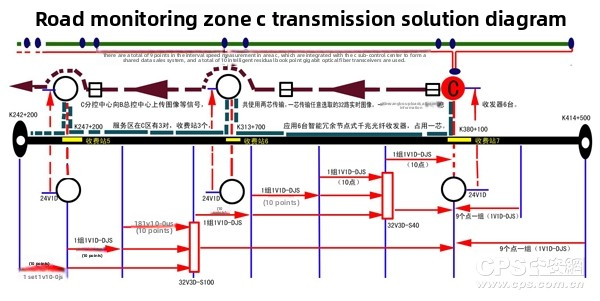
The equipment in areas A, B and C is configured according to the above diagram. Therefore, due to the large number of optical-level cascaded transmission video signals and the large number of electrical-level cascaded transmission nodes with long distances, the images of service areas, toll stations and other signals are transmitted using intelligent redundant node gigabit transceivers for upload to the monitoring center. The monitoring center and the main monitoring center form two sets of gigabit full-speed optical fiber networks, using intelligent redundant node gigabit transceivers for transmission. The intelligent redundant node gigabit transceivers are used for interval speed measurement. When the distance exceeds 100km, to ensure transmission quality, additional nodes are added for relay transmission.
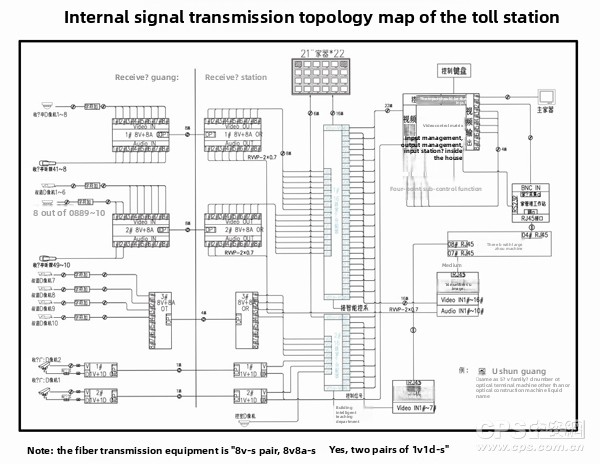
Highway toll station signal transmission structure diagram - Application of optical transceiver is shown in Figure 7:
Highway toll station signal transmission structure diagram - Application of optical fiber transceiver is shown in Figure 8:
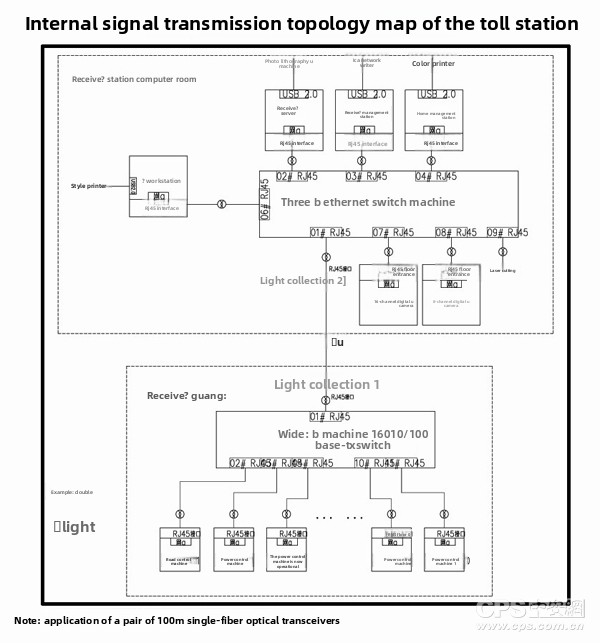
TAG:
Since 2008, China has fully entered the "highway era". The construction of highways across the country has been blooming like bamboo shoots after a spring rain for five consecutive years, gradually forming a beautiful highway network in China. Further improving the physical and technical defense levels of highways and establishing a networked, high-definition and intelligent highway video monitoring system have become one of the core projects of highway construction. The quality of the transmission system will fundamentally affect and determine the safety and practicality of the overall plan. The design scheme of the optical fiber transmission system for the video monitoring of the Ordos highway was proposed, which adopted an industrial transmission scheme mode, making the overall scheme more practical and stable. Technology is the first driving force of production. The development of technology and the application of new technologies will better promote the increasingly perfect and mature intelligent highway management system with a reliable and safe highway transmission system.








