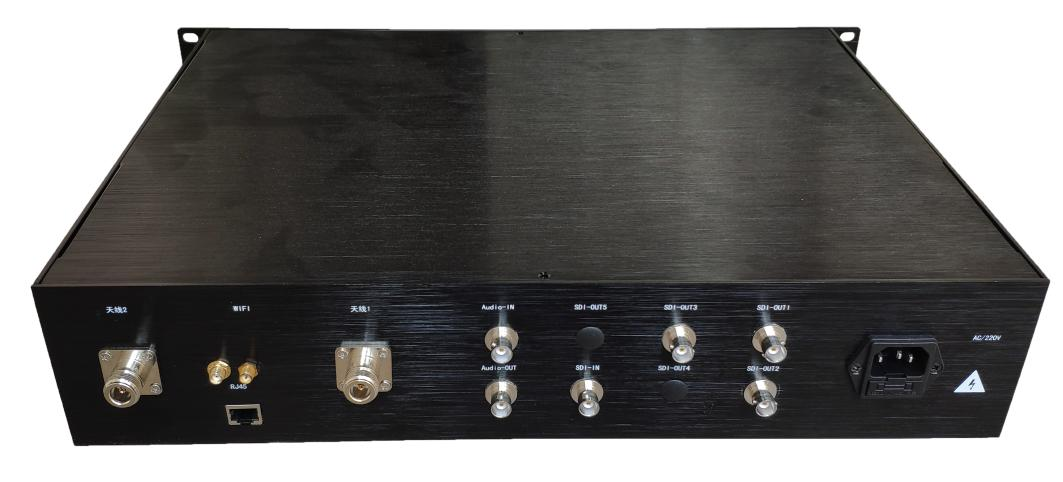
A Single Article to Understand Mesh Wireless Networking
For small-sized ordinary households, wireless networking has traditionally been implemented by placing the wireless router in the central position of the house, which can basically achieve full network coverage throughout the house. However, for large-sized houses or buildings with complex structures, network setup is necessary to achieve full network coverage throughout the house. The traditional expansion network methods, such as relaying and bridging, are highly dependent on the main router and cannot achieve seamless switching. Mesh routing can solve these problems.
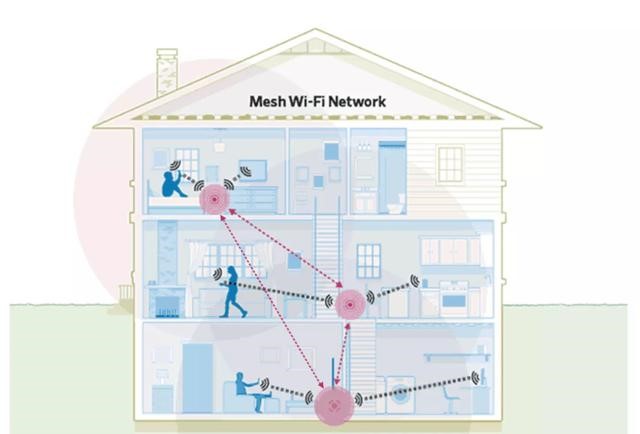
What is a Mesh Network
Mesh network, also known as "wireless mesh network", is a "multi-hop" network that evolved from ad-hoc networks. In an ad-hoc network, each node is mobile and can dynamically maintain connections with other nodes in any way. During the evolution of the network, wireless technology is an indispensable component. Wireless Mesh can collaborate with other networks for communication, forming a dynamic and expandable network architecture, and maintaining wireless connectivity between any two devices.
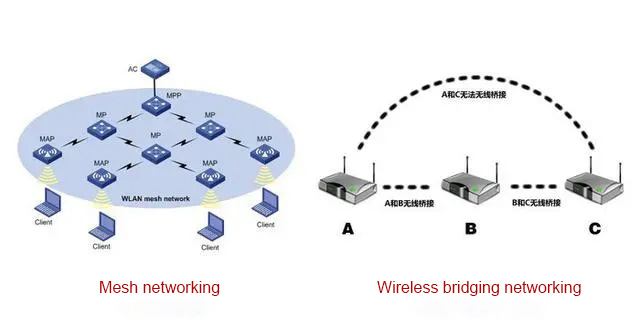
The operating principle of Mesh wireless networking
The Mesh wireless transmission frequency band is 1.4 GHz. In Mesh networking, the highest bandwidth of 40M is used for high-speed data transmission between wireless access points, and for medium-speed data transmission between access points and terminals.
Traditional wireless networking issues
Relay connection: Although it can unify the SSID name, the devices cannot intelligently switch to the best signal source, and the network quality is prone to deteriorate.
Bridge connection: The SSID names cannot be unified. When switching Wi-Fi networks, you need to disconnect and reconnect.
Wired expansion AP: It must be planned during the decoration and wiring process. There will be no possibility of expansion later.
The advantages of Mesh networking
Deployment is simple: The design goal of the Mesh network is to minimize the number of wired devices and wired wireless access points, thereby significantly reducing the total cost of ownership and installation time.
High stability: The Mesh network is more robust than the single-hop network because it does not rely on the performance of a single node.
Flexible structure: In a multi-hop network, devices can simultaneously connect to the network through different nodes.
Ultra-high bandwidth: A single node not only can transmit and receive information, but also can act as a router to forward information to nearby nodes. As more nodes are interconnected and the possible number of paths increases, the total bandwidth also significantly increases.
-
2025-10-28
-

What Is a Mesh Network Radio and How Does It Work?
2025-10-14 -

How to Set Up a Wireless Self-Networking Station in Remote Areas
2025-09-16 -

What Is an Outdoor Wireless Bridge?
2025-08-29 -
MESH Self-Organizing Network Communication Systems: Principles and Future Prospects
2025-08-18 -

Understanding the 4 Major Types of Microwave Transmission
2025-07-30










