Introduction to the Basic Communication Principles of Wireless Microwave
When it comes to microwave communication, most people are relatively unfamiliar with it. Many often mistake it for mobile communication base stations. However, if you observe carefully, you will notice that on the rooftops of some buildings, apart from base stations, there are also some devices resembling "big drums". In some remote areas, such drum-like devices are even more common. To be precise, we usually call them "microwave communication antennas". Only when you approach and look closely with your mobile phone can you get a good look at them.
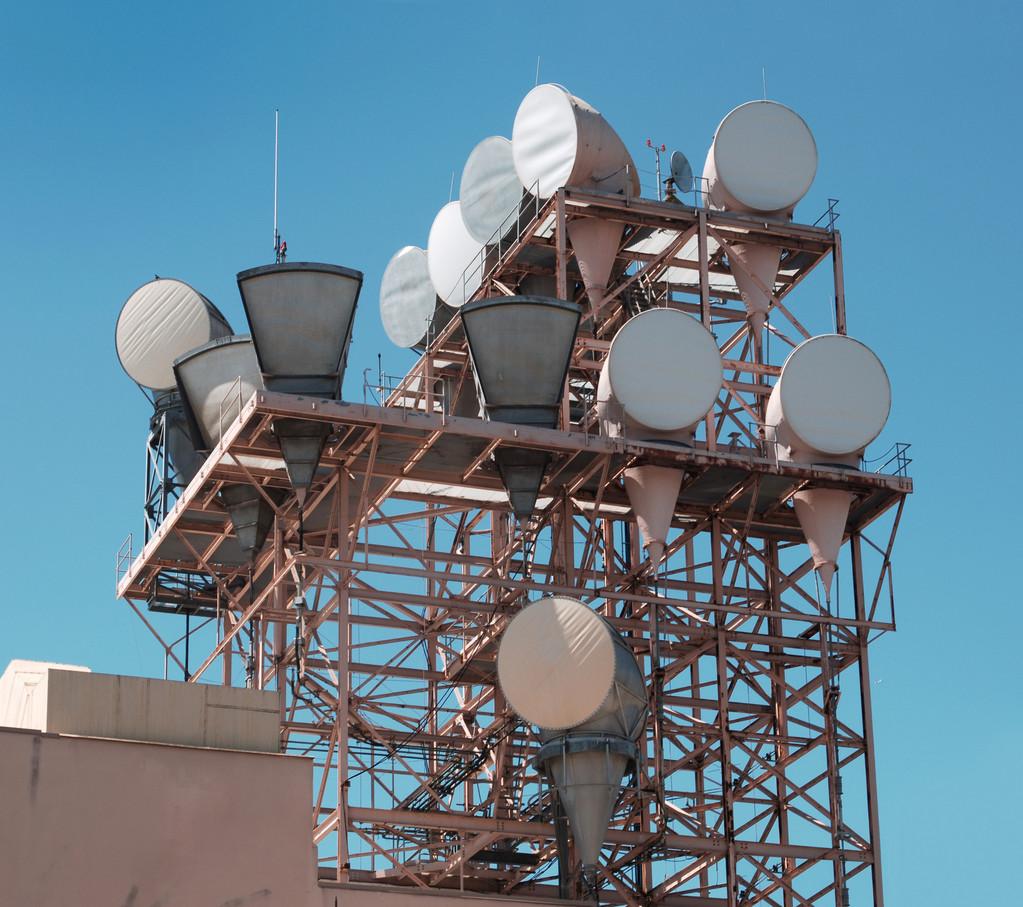

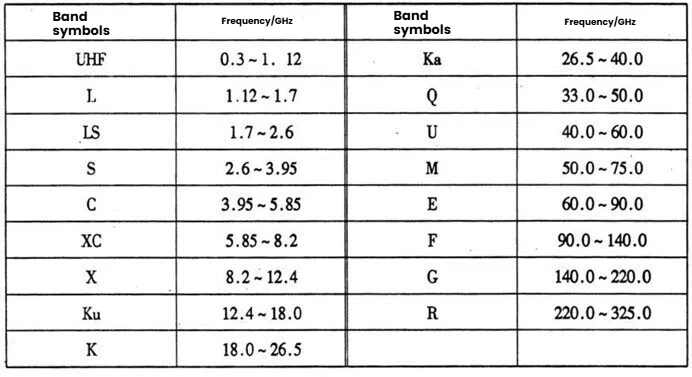
Microwave communication, in English, is referred to as electromagnetic waves with wavelengths ranging from 0.1 to 1 meter. It is a method of relay communication where microwaves (Microwave) act as the carrier to transmit information. Depending on the frequency band, engineers have also specifically defined the bands.
Unlike modern communication networks such as coaxial cable communication, optical fiber communication and satellite communication, microwave communication directly uses microwaves as the medium for communication. It does not require solid media. When there are no obstructions within the straight-line distance between two points, microwaves can be used for transmission. Utilizing microwaves for communication has the characteristics of large capacity, good quality and the ability to transmit over long distances. Therefore, it is an important communication means of national communication networks and is also widely applicable to various dedicated communication networks.
The emergence of microwaves
In 1901, Marconi conducted the world's first transatlantic radio communication experiment using 800 KHz medium-wave signals from Britain to Newfoundland in North America, marking the beginning of a new era in human wireless communication. Initially, humans generally used long waves and medium waves for communication, and it was not until the early 1920s that short-wave communication was discovered.

(In 1945, the microwave communication equipment of the US military)
In 1931, the world's first microwave communication circuit was established between Dover, UK and Calais, France. Microwave communication entered a new era. After World War II, microwave relay communication developed rapidly. In 1947, the renowned Bell Laboratories in the United States established the world's first analog microwave communication line between New York and Boston.
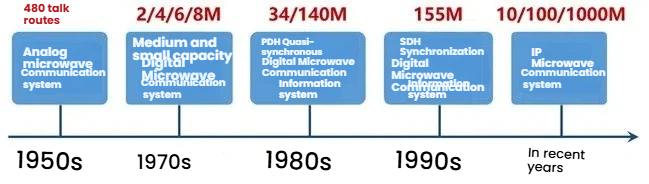
In 1955, tropospheric scattering communication was successfully tested in North America. Satellite communication experiments began in the 1950s and were put into use in the mid-1960s. Due to the extremely abundant frequency resources in the microwave band and the extremely crowded spectrum below the microwave band, mobile communication and other technologies also developed towards the microwave band. Moreover, the development of digital technology and microelectronics technology also promoted the gradual transition of microwave communication from analog microwave communication to digital microwave communication. In 1947, the renowned Bell Laboratories in the United States established the world's first analog microwave communication line between New York and Boston. By the end of the 1950s, countries such as Australia, the United Kingdom, Canada, France, Italy, and Japan had installed microwave relay communication systems on their main trunk routes.

Compared with other countries, our country's research on microwave communication is relatively complete. It began only in the 1960s. Currently, analog microwave has gradually been replaced by digital microwave communication, and humanity has entered the era of digital microwave communication. Digital microwave communication is divided into two stages: PDH (pseudo-synchronous) and SDH (synchronous). From the late 1980s to the beginning of this century, SDH gradually took the dominant position in the transmission system, and the development of microwave communication technology has entered an acceleration period.
Currently, microwave communication technology and wired communication technology have both entered the IP era. The wired transmission network dominated by optical fiber communication has taken the lead, becoming the essential network transmission method in households of all sizes. However, for remote areas, due to the high cost of setting up wired transmission and the susceptibility to natural environments, microwave communication is still used for transmission.
Three major communications
Compared with optical fiber communication, the inherent characteristics of microwave communication have unique advantages that cannot be replaced. However, it is inferior in terms of resistance to natural disasters and flexibility. Nevertheless, optical fiber significantly ensures the advantages of high-speed transmission and high bandwidth. However, in terms of investment cost and duration, it requires a significant amount of resources.
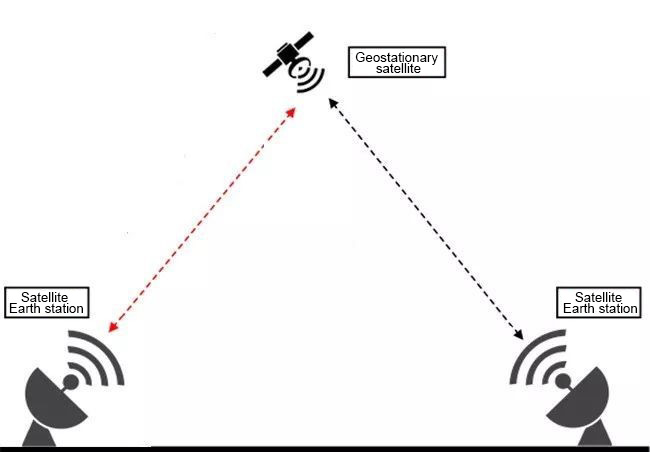
As far as the three major communication transmission systems we currently know are concerned, namely optical fiber communication, microwave communication and satellite communication, but in fact, satellite communication is also a type of microwave communication.
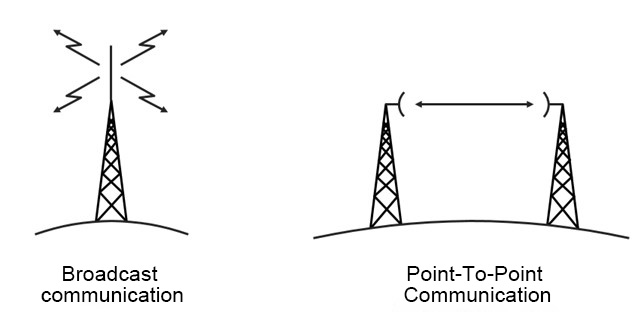
In electromagnetic wave communication, it can generally be divided into broadcasting mode and point-to-point mode. However, microwave communication is transmitted in a point-to-point manner. This mode is determined by the characteristics of microwaves themselves. Due to their high frequency and short wavelength, they inherently have poor diffraction ability and weak penetration power. When transmitted over the ground, they experience significant attenuation and have a short transmission distance. Many people might think that electromagnetic waves can be propagated over long distances using the reflection method in the ionosphere in the sky. However, microwaves have such a high frequency that the ionosphere cannot effectively reflect (it can only penetrate), so a relay method is generally used for signal relay, achieving limited line-of-sight transmission, which is the point-to-point transmission visible to the naked eye.
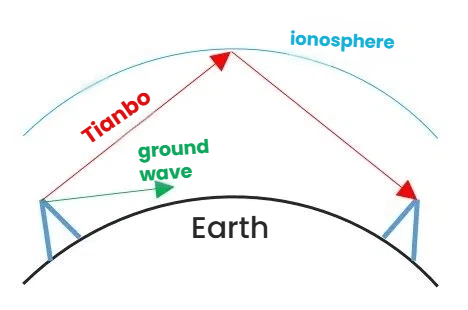
Of course, this characteristic transmission feature is also known as microwave relay communication or microwave relay transmission. Based on the fact that microwaves cannot reflect the ionosphere but can only penetrate through it, if we place this relay and transmission equipment in the sky, then it would be possible to conduct long-distance communication. Exactly, it is satellite communication.
The composition of microwave equipment
Generally speaking, microwave equipment is mainly composed of IDU, ODU, intermediate frequency cables, antennas, and other components.
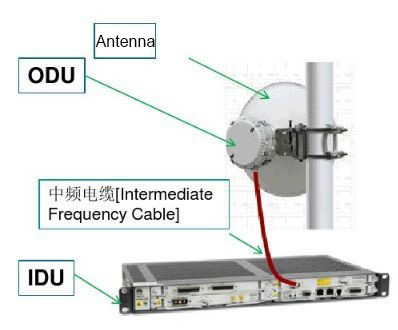
IDU stands for Indoor Unit. ODU stands for Outdoor Unit. Intermediate frequency refers to the process where the transmitter converts the signal carrier into the transmission frequency, or converts the receiving frequency into the baseband. This intermediate frequency is generally determined by the system architecture.
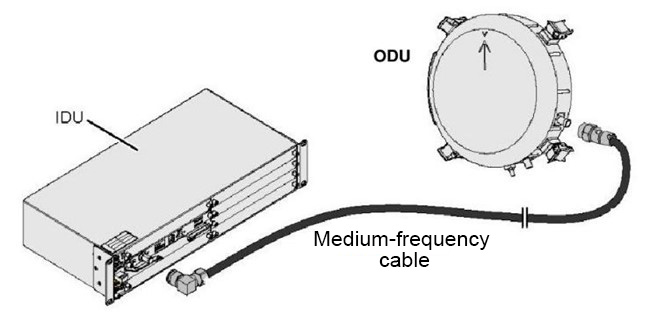
RF refers to the frequency of the electromagnetic wave signal emitted by the antenna and propagating in the air. The IDU is responsible for completing service access, multiplexing and demultiplexing, and converting the service signal into intermediate frequency analog signals in the indoor environment.
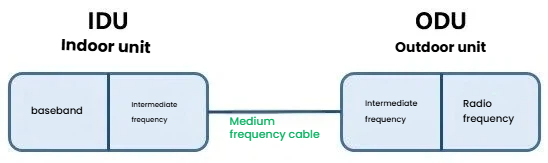
The ODU is responsible for performing frequency conversion and amplification of the signal. The antenna converts the radio frequency signal into electromagnetic waves and radiates them into the air. Or it receives the electromagnetic waves, converts them into radio frequency signals, and transmits them to the ODU.
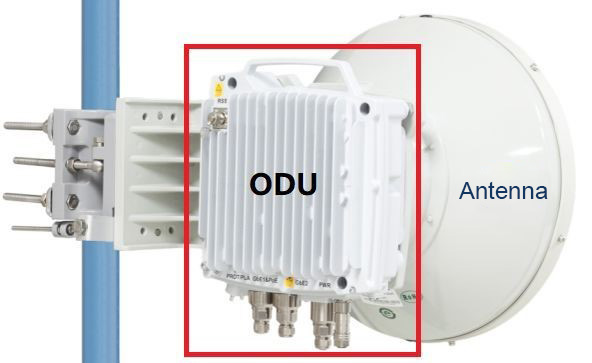
Microwave antennas include not only the drum-shaped antennas, but also parabolic antennas and Cassegrain antennas. Satellite communications are usually large dishes. The installation methods for outdoor microwave equipment also come in two types.

One type is the separate installation where the ODU and the antenna are separated. The other type is the direct fastening installation where the ODU and the antenna are fastened together.
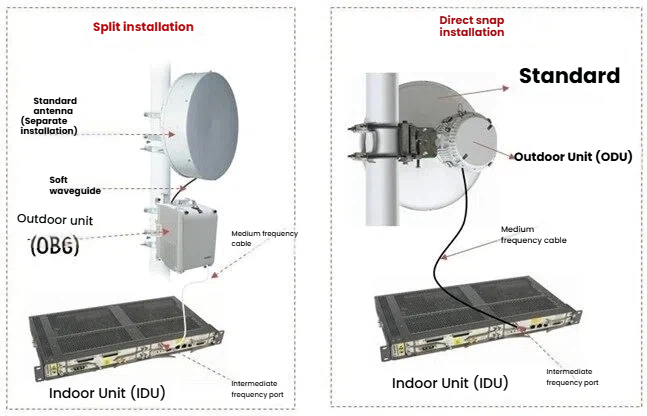
When there are two ODU (used for 1+1 HSB hot backup or 1+1 FD frequency division), there will also be a combiner for power distribution or synthesis. 1+1 HSB hot backup (one primary and one backup to prevent service interruption in case of ODU failure) in microwave communication, the sites are divided into three types: terminal station, relay station, and hub station.
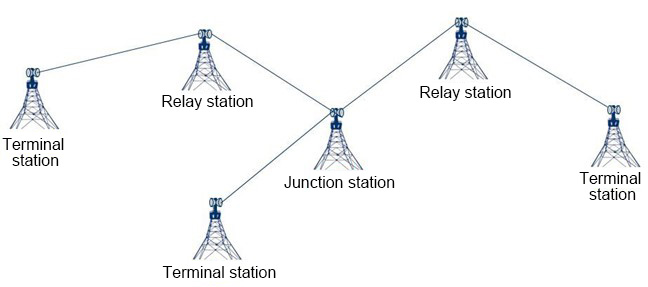
Relay stations and hub stations both involve signal forwarding (reception). The methods of relay can be classified as passive and active. Passive relays include the passive reflectors we saw in the diagram, as well as back-to-back antennas. For active relays, they are divided into regenerative relays, intermediate frequency relays, and radio frequency relays. The term "active" means there is an energy source and power supply, which means it has been strengthened through an external energy source. Although the effect is better, the cost is higher, and there are more failure points.
-
 2025-10-24
2025-10-24 -

What is an Emergency Communication System and How Does It Work?
2025-09-16 -

What Is Point to Point and Point to Multipoint Wireless Network?
2025-09-05 -

What Are the Two Types of Microwave Transmission?
2025-08-29 -

Multi-Node MESH Networking: Principles and Real-World Applications
2025-08-18 -

What Is the Difference Between Radio and Microwave Video Transmission?
2025-07-30 -

Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Transmission Equipment Communication Solution
2025-07-24








