News Center
-
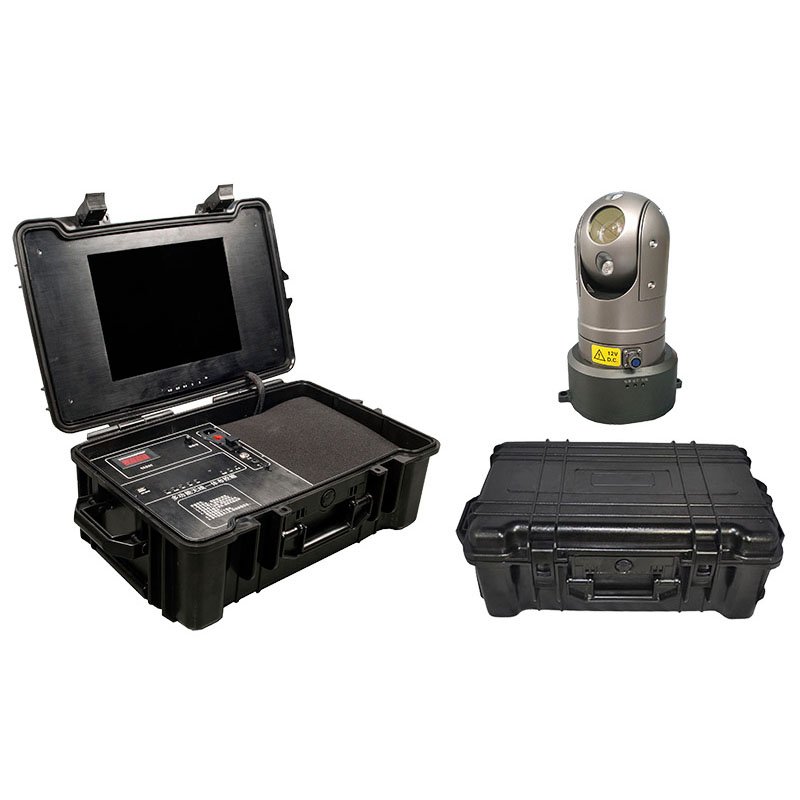 2026-01-19As wireless communication continues to evolve toward higher bandwidth, intelligence, and decentralization, traditional systems that rely on fixed base stations or single relay points are increasingly unable to meet the demands of complex and dynamic communication environments.
2026-01-19As wireless communication continues to evolve toward higher bandwidth, intelligence, and decentralization, traditional systems that rely on fixed base stations or single relay points are increasingly unable to meet the demands of complex and dynamic communication environments. -
2025-12-29
Role of Wireless Point-to-Point Networks and Microwave Transmission in Remote Internet Access
With the rise of remote work and digital business, point-to-point internet access has become a crucial infrastructure. Wireless Point-to-Point Networks and Point-to-Point Wireless technologies enable stable internet access in urban, rural, and remote areas, supporting high-definition video transmission, cloud computing, and IoT applications. -
2025-12-23
Application of Point-to-Point Wireless Networks in Industrial Communication
In modern industrial environments, stable and low-latency data communication is crucial for production efficiency and safety. Point-to-Point Wireless Networks and Wireless Point-to-Point Networks have become core technologies for industrial communication. These networks enable high-speed and secure data transmission across production areas, reducing wiring costs and adapting to communication needs in complex environments. -
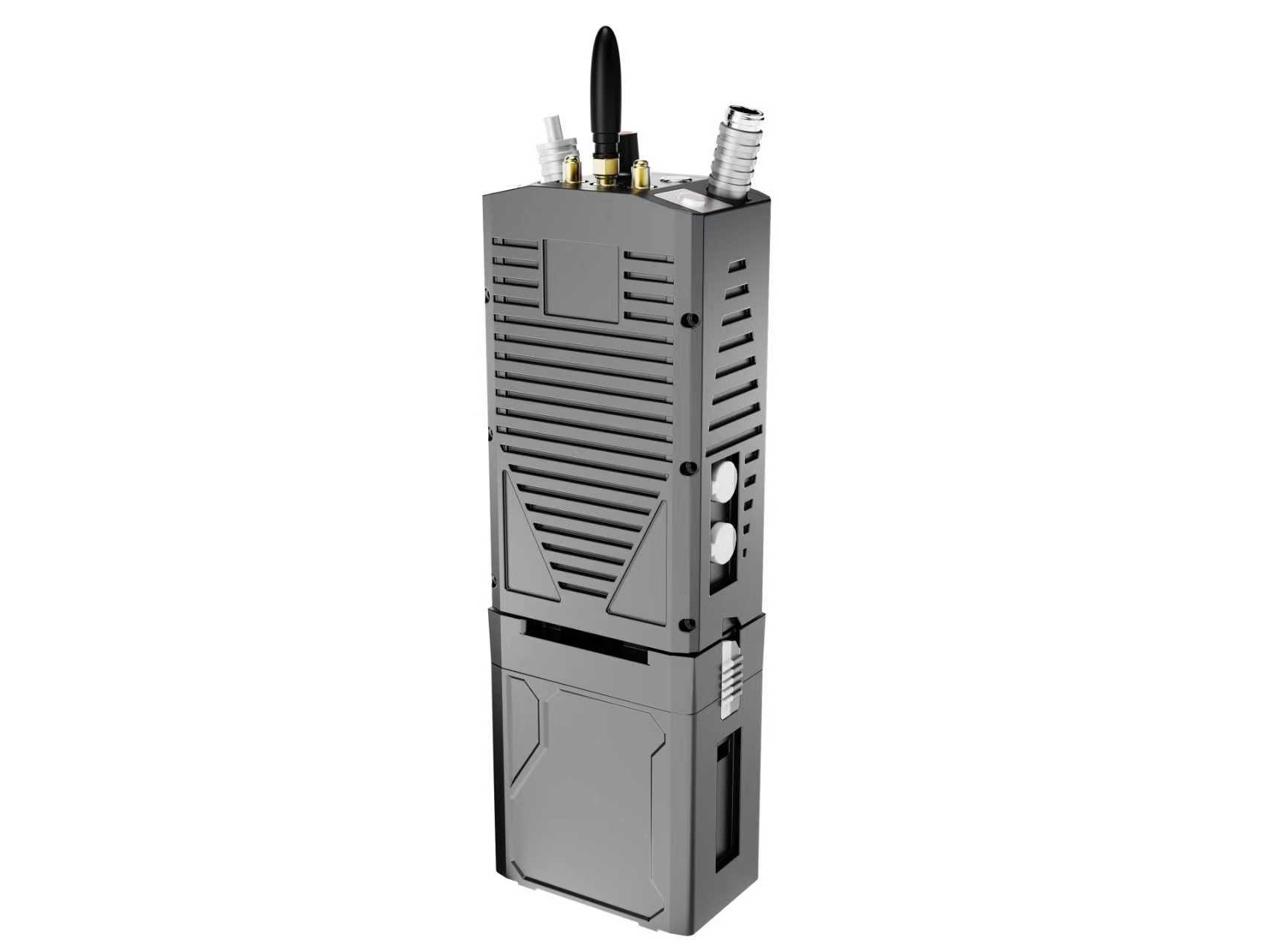 2025-12-22
2025-12-22UAV Data Transmission and Point-to-Point Wireless Network Technology Trends
With the widespread use of UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) in logistics, surveying, and emergency response, efficient data transmission has become a critical requirement. UAV Data Transmission Stations are gradually becoming an essential component of the UAV ecosystem. Through reliable Point-to-Point Wireless Networks, UAVs can transmit collected data in real time to ground control centers, ensuring accuracy and operational efficiency. -
 2025-12-22
2025-12-22Install wireless surveillance. Use the 5.8G wireless bridge. It's very reliable!
In recent years, the demand for wireless monitoring has become increasingly strong, which has led to a significant increase in the shipment of wireless bridges. The technical requirements for wireless bridges in the market have also become more stringent. Wireless monitoring is mostly used for remote unmanned monitoring, and the equipment... -
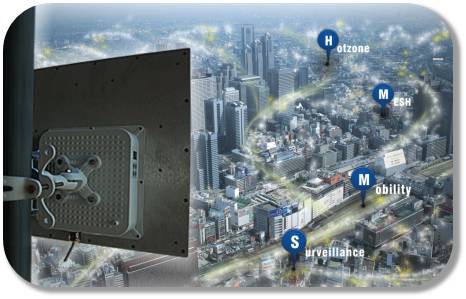 2025-12-21
2025-12-21There are four common signal transmission methods used in wireless monitoring that you may not be aware of!
The layout of wireless monitoring will vary depending on the specific environment of the client. The correct construction plan will not only enhance the stability of the monitoring system, but also improve the construction efficiency and reduce costs. Below, ... -
 2025-12-21
2025-12-21How to install a wireless bridge in an elevator? This is how professionals do it!
Wireless bridge is a dedicated wireless transmission device specifically designed for elevator wireless video and elevator Internet of Things transmission. Compared with the traditional elevator cable data transmission solution, it has strong anti-interference ability, long transmission distance, high cost performance, and convenient construction... -
 2025-12-20
2025-12-20Using wireless bridges in this way can significantly reduce the overall cost!
The rapid economic development has led to a continuous increase in living costs. Correspondingly, labor costs and construction expenses are also rising steadily. The general conditions for outdoor construction are also quite challenging. In summary, the construction costs will only continue to increase in the future...









